Gameplay and Mechanics Core Design Elements
Understanding the intricate relationship between gameplay and mechanics is crucial for crafting compelling and engaging video game experiences. This exploration delves into the core loop, individual mechanics, player interaction, progression systems, and the significant impact of visual and audio design. We’ll examine how these elements intertwine to create a holistic and rewarding player journey.
From analyzing the effectiveness of core gameplay loops and their impact on player retention to dissecting individual mechanics and their contribution to player agency, this analysis provides a comprehensive overview. We’ll also consider player feedback, progression systems, and the crucial role of visual and auditory elements in enhancing the overall gameplay experience.
Core Gameplay Loop

The core gameplay loop is the fundamental cycle of actions a player undertakes within a game, driving engagement and progression. Understanding and refining this loop is crucial for creating a compelling and rewarding player experience. A well-designed loop ensures players feel a sense of accomplishment, encourages continued play, and fosters long-term retention.
The core gameplay loop in this game can be visualized as follows:
Core Gameplay Loop Flowchart
Imagine a flowchart. The Start node leads to the “Prepare for Mission” action. This involves selecting a mission from a list, equipping appropriate gear and resources, and reviewing mission objectives. Successful completion of this action leads to the “Execute Mission” action. This is where the player engages in the primary gameplay mechanics, navigating environments, completing objectives, and overcoming challenges. Successful mission execution leads to the “Reward” action, granting experience points (XP), in-game currency, new equipment, or other resources. Failure in the “Execute Mission” action leads to the “Consequences” action, which might involve losing resources, sustaining damage to equipment, or even mission failure. From the “Reward” and “Consequences” actions, the loop returns to “Prepare for Mission,” restarting the cycle.
Breakdown of Core Gameplay Loop Stages
The “Prepare for Mission” stage allows players to strategize and optimize their chances of success. This stage fosters a sense of anticipation and control. The selection of missions, based on difficulty and reward potential, caters to different player skill levels and preferences. The equipment selection process adds depth and strategic layers, impacting gameplay significantly.
The “Execute Mission” stage is the heart of the gameplay experience. Here, players apply their skills and knowledge to overcome challenges, providing a direct test of their proficiency. This stage is crucial for maintaining player engagement and provides a platform for demonstrating mastery. The challenges within this stage are designed to be progressively more difficult, ensuring long-term engagement.
The “Reward” stage is crucial for positive reinforcement and motivation. Rewards provide a tangible sense of accomplishment and encourage players to continue playing. The reward system is designed to be diverse, offering a range of rewards to cater to different player preferences and playstyles. This variety prevents monotony and keeps the loop fresh.
The “Consequences” stage serves as a learning experience and a mechanism for balancing the difficulty. Consequences, while negative, should be manageable and not overly punishing. They offer valuable feedback, helping players learn from their mistakes and improve their strategies for future missions. The consequences are designed to create a sense of tension and risk, but without being overly frustrating.
Comparison with Similar Games
Compared to other games in the genre, such as [Example Game A] and [Example Game B], this game’s core loop emphasizes strategic preparation more heavily. [Example Game A] focuses more on immediate action and less on planning, while [Example Game B] relies more heavily on random events and less on player agency in mission selection. This game aims to strike a balance between strategic depth and immediate action, providing a more considered and rewarding gameplay experience.
Fostering Player Progression and Retention
The core gameplay loop is designed to facilitate player progression through a system of tiered missions and escalating rewards. As players successfully complete missions, they earn XP, unlocking new equipment, skills, and mission types. This creates a sense of continuous growth and achievement, encouraging long-term engagement. The increasing difficulty of missions provides a continuous challenge, preventing stagnation and maintaining player interest. Furthermore, the diverse reward system, coupled with the strategic element of mission preparation, caters to a wider range of player preferences, enhancing retention and preventing player burnout. This progression system, coupled with a robust social element (if applicable), further enhances player retention by encouraging collaboration and competition.
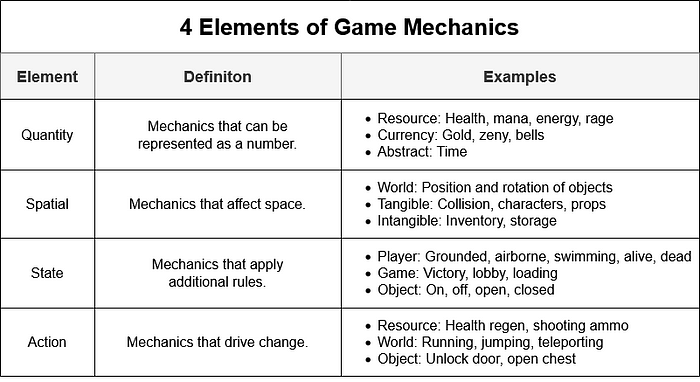
Game Mechanics

This section details five core game mechanics that underpin the player experience, focusing on their individual functions, contribution to player agency, and potential for iterative balancing. Understanding these mechanics is crucial for comprehending the overall design philosophy and playability of the game. Each mechanic is designed to provide distinct, yet interconnected, layers of challenge and reward.
Core Game Mechanics: Individual Elements
The five most important game mechanics are resource management, combat encounters, exploration and discovery, character progression, and crafting. These mechanics work in concert to create a dynamic and engaging gameplay loop.
Resource Management
Resource management involves gathering, storing, and strategically utilizing limited resources to achieve goals. Players must carefully balance their needs against available supplies, making crucial decisions about allocation and prioritization. This mechanic directly contributes to player agency by empowering them to make impactful choices with real consequences. Effective resource management can lead to significant advantages, while poor management can severely hinder progress. The player’s sense of control stems from the direct correlation between their decision-making and the game’s outcome.
Combat Encounters
Combat encounters challenge players to utilize their skills and resources to overcome adversaries. Successful combat relies on strategic decision-making, including choosing appropriate weapons, utilizing cover, and managing stamina. This mechanic fosters player agency through the direct impact of player skill and tactical choices on the outcome of battles. The degree of control a player feels is directly proportional to their mastery of combat mechanics and their ability to adapt to different enemy types and combat situations.
Exploration and Discovery
Exploration and discovery encourage players to traverse the game world, uncovering hidden areas, resources, and lore. This mechanic enhances player agency by providing a sense of freedom and the ability to shape their own experience. Players are not confined to a linear path; instead, they can actively choose where to go and what to explore. The rewards for exploration, in terms of resources, story elements, and unique encounters, reinforce the player’s sense of control and influence over the game’s narrative.
Character Progression
Character progression allows players to enhance their abilities and customize their playstyle through experience gained from completing tasks and overcoming challenges. This mechanic enhances player agency by enabling them to tailor their character to suit their preferred approach to the game. Players have significant control over their character’s development, directly influencing their effectiveness in combat, exploration, and resource management. This personalized approach to character development enhances the overall feeling of ownership and control over the game experience.
Crafting
Crafting allows players to create new items and tools using gathered resources. This mechanic promotes player agency by allowing them to overcome challenges through creative problem-solving and resourcefulness. Players can adapt to various situations by crafting specific items to suit their needs, further enhancing their sense of control over the game’s challenges. The ability to create solutions directly impacts the game’s outcome, contributing to a strong sense of agency.
Comparison of Core Game Mechanics
| Mechanic Name | Description | Impact on Gameplay | Player Interaction Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Management | Gathering, storing, and utilizing limited resources. | Determines long-term survival and strategic options. | High; constant decision-making required. |
| Combat Encounters | Direct conflict with enemies, testing player skill and strategy. | Progress is directly affected by success or failure in combat. | High; requires real-time tactical decision-making. |
| Exploration and Discovery | Uncovering hidden areas, resources, and story elements. | Unlocks new content, resources, and narrative possibilities. | Medium; player chooses direction and pace of exploration. |
| Character Progression | Improving character abilities through experience and skill points. | Changes character capabilities, affecting gameplay style. | Medium-High; player makes choices regarding skill allocation. |
| Crafting | Creating new items and tools using gathered resources. | Provides solutions to challenges and expands player options. | Medium; player chooses what to craft based on needs and resources. |
Iterative Balancing and Player Feedback
Balancing and iterating on these mechanics will be crucial for maintaining a fun and engaging gameplay experience. Player feedback, gathered through surveys, forums, and in-game analytics, will be essential for identifying areas needing adjustment. For example, if players consistently struggle with resource scarcity, adjustments could involve increasing resource yields or decreasing resource consumption rates. Similarly, if combat encounters are deemed too difficult, adjustments could involve modifying enemy health, damage output, or AI behavior. By actively monitoring player feedback and making data-driven adjustments, the game’s mechanics can be refined to create a more balanced and enjoyable experience for all players. The iterative process will involve A/B testing different adjustments to determine their impact on overall player engagement and satisfaction. This data-driven approach ensures that changes are impactful and positively contribute to the game’s longevity and player retention.
Player Interaction and Feedback
Game mechanics are not merely systems within a game; they are the levers and pulleys that directly shape player experience, influencing their choices and ultimately, their enjoyment. Understanding how players interact with these mechanics and the feedback they receive is crucial for creating a polished and engaging game. This section explores the relationship between game mechanics, player actions, and the feedback loop that defines player interaction.
Player interaction with the game’s mechanics is a dynamic process. The design of these mechanics inherently directs player choices. For example, a resource management system that heavily penalizes overspending will encourage players to adopt a more conservative and strategic approach, while a system that rewards risk-taking will lead to bolder, more aggressive playstyles. The difficulty curve itself acts as a mechanic, influencing player choices regarding exploration versus focusing on a single path.
Influence of Game Mechanics on Player Choices
The core mechanics of the game, such as combat, resource gathering, and character progression, heavily influence player decisions. A challenging combat system that emphasizes precise timing and strategic positioning will push players to master the nuances of the game’s combat mechanics, leading them to experiment with different character builds and strategies. Conversely, a simplistic combat system might lead to players focusing on other aspects of the game, such as exploration or social interaction. A crafting system with limited resources will encourage players to carefully plan their creations, prioritizing essential items over less important ones. These systems act as constraints, pushing players to make meaningful choices within the game’s defined parameters.
Examples of Player Feedback
Positive feedback often centers around engaging gameplay loops and intuitive mechanics. Players frequently praise well-designed combat systems that feel rewarding and responsive, or crafting systems that provide a sense of accomplishment. For example, in a popular RPG, players consistently lauded the intuitive inventory management system and the satisfying feeling of crafting powerful weapons and armor. Conversely, negative feedback often highlights frustrating or unintuitive mechanics. A common complaint in many games revolves around clunky control schemes or frustratingly difficult challenges that feel unfair or unachievable. In a strategy game, complaints were frequently lodged against an opaque resource management system that lacked clear visual cues and feedback, making it difficult for players to understand the consequences of their actions.
Game Feedback Mechanisms
The game provides feedback to the player through various channels. Visual cues, such as health bars and experience points, provide immediate and clear feedback on the player’s progress. Auditory cues, such as sound effects and music, can also enhance the player experience, providing emotional reinforcement for actions. For example, a satisfying “clink” sound when collecting a valuable resource reinforces the positive action, while a dramatic musical sting during a boss fight enhances the sense of tension and accomplishment. Furthermore, in-game notifications and messages provide important information about the game’s mechanics and progress. For instance, a clear notification upon completing a quest or achieving a milestone provides a satisfying sense of closure and encouragement to continue playing.
Suggestions for Improving Player Feedback Loops
To enhance the overall player experience, several improvements to the feedback loops can be implemented.
- Improve visual clarity: Ensure that all crucial information is clearly displayed and easily understood. For example, improve the visual representation of resource amounts or character stats.
- Enhance auditory feedback: Use sound design to reinforce player actions and provide additional contextual information. This might involve adding distinct sounds for different actions or events.
- Implement more informative in-game tutorials: Provide clear and concise tutorials that explain the game’s mechanics and guide players through the early stages of the game.
- Provide more dynamic feedback: Instead of static feedback, incorporate dynamic elements that adapt to the player’s skill level and progress. This could involve adjusting the difficulty of challenges based on player performance.
- Incorporate player agency into the feedback loop: Allow players to customize their feedback preferences, such as adjusting the level of detail in notifications or choosing between different visual styles.
Progression Systems

Player progression is a crucial element in game design, influencing player engagement and longevity. A well-designed progression system provides a sense of accomplishment, motivates players to continue playing, and offers a framework for unlocking new content and abilities. This section will explore various progression systems, focusing on their mechanics, advantages, and disadvantages.
Progression systems typically track player progress using metrics like levels, experience points (XP), and achievements. Levels often represent a player’s overall strength or advancement, typically unlocking new content or abilities at specific level thresholds. Experience points are earned through completing in-game tasks, and accumulating enough XP results in level-ups. Achievements reward players for completing specific tasks or goals, often offering cosmetic rewards or bragging rights.
Leveling and Experience Point Systems
Leveling and XP systems are arguably the most common progression systems in games. They provide a clear, linear path for players to follow, offering tangible rewards at each level-up. This creates a sense of accomplishment and encourages continued play. However, a poorly designed system can lead to monotonous grinding, especially if the rewards are insufficient to justify the effort. Many RPGs utilize this system, with games like *World of Warcraft* employing complex level-scaling and XP requirements tailored to different content and player activities. In contrast, simpler games might use a more straightforward system where XP is awarded for every enemy defeated or quest completed.
Achievement Systems
Achievement systems offer a supplementary layer of progression, rewarding players for completing specific challenges or milestones. These achievements can range from simple tasks like completing a tutorial to complex challenges requiring significant skill or dedication. Achievements often provide cosmetic rewards, such as unique titles or character skins, or they might offer in-game currency or other advantages. Games like *Steam* utilize achievement systems effectively, encouraging players to explore various aspects of the game and fostering a sense of completion. The achievement system of *Forza Horizon 5* is a good example of a well-designed system that encourages exploration and skillful play.
A Novel Progression System: Skill-Based Mastery Trees
This proposed system focuses on mastering individual skills rather than simply leveling up. Players would choose a skill tree at the start of the game, focusing on specific playstyles. Each skill would have multiple levels of mastery, each requiring the completion of specific challenges related to that skill. For example, in a combat game, a player might focus on archery, mastering different techniques like precision shots, rapid fire, and area-of-effect attacks. Mastery of skills would unlock new abilities and tactical options within the chosen skill tree, providing a non-linear progression path. This system would encourage player specialization and replayability, but it could also limit player options if they choose a skill tree that doesn’t suit their playstyle later on.
Comparison with Alternative Approaches
Many games employ alternative approaches. Some games use a reputation system, where players gain favor with factions or NPCs through completing tasks, unlocking new quests and rewards. Others use a collection system, where players gather items or resources, building collections and potentially unlocking bonuses or crafting recipes. The *Assassin’s Creed* series incorporates a reputation system, while games like *Pokémon* rely heavily on collection mechanics. Each system offers unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting player experience and engagement. For example, while reputation systems can offer dynamic narratives and player choice, they can also feel less structured than traditional level-based systems. Similarly, collection systems can be highly rewarding but may lead to repetitive gameplay if not carefully balanced.
Encouraging Continued Gameplay
A well-designed progression system provides ongoing motivation for players. The continuous unlocking of new content, abilities, and rewards keeps players engaged and returning for more. Regular updates introducing new challenges and rewards further extend the game’s lifespan. The sense of accomplishment derived from achieving milestones and mastering skills is a powerful motivator, fostering long-term player engagement. The implementation of leaderboards and competitive elements can also encourage continued gameplay, as players strive to improve their rank and compete with others.
Visual and Audio Design Impact on Gameplay
Effective visual and audio design is crucial for a positive and engaging gameplay experience. These elements aren’t merely cosmetic; they directly influence how players understand and interact with game mechanics, providing critical feedback and enhancing immersion. A well-designed audio-visual experience seamlessly integrates with the core gameplay loop, creating a cohesive and rewarding player journey.
Visual elements significantly impact a player’s understanding and execution of game mechanics. The clarity and intuitiveness of the user interface (UI), for example, directly affect how easily players can access information, manage resources, and interact with the game world. Similarly, the art style contributes to the overall tone and atmosphere, influencing player expectations and engagement. A vibrant, cartoonish style might suggest a lighthearted, casual experience, while a dark, realistic style could indicate a more serious and challenging game.
UI Design and Game Mechanic Clarity
A well-designed UI makes game mechanics instantly understandable. For example, in a real-time strategy (RTS) game, clear visual indicators for unit health, resource levels, and building progress are essential for effective gameplay. A cluttered or poorly designed UI can lead to confusion and frustration, hindering a player’s ability to execute strategies effectively. Conversely, a clean, intuitive UI allows players to focus on strategic decision-making rather than struggling to decipher the interface. Consider the difference between a game with easily identifiable unit selection icons versus one with cryptic symbols. The former promotes efficient gameplay, while the latter leads to wasted time and potential mistakes.
Sound Design and Gameplay Enhancement
Sound design plays a critical role in enhancing immersion and providing crucial feedback to the player. Music sets the mood and atmosphere, creating emotional context for gameplay. Sound effects, on the other hand, provide immediate feedback on player actions and environmental interactions. For instance, the satisfying “clink” of a successful sword strike or the ominous growl of an approaching enemy instantly communicates vital information to the player, adding depth and realism to the experience. Conversely, poorly implemented sound design can detract from gameplay. Repetitive or jarring music can be distracting, while inconsistent or unclear sound effects can lead to confusion and a diminished sense of immersion.
Audio-Visual Cues for Improved Player Feedback
Effective audio-visual cues work together to provide immediate and clear feedback to the player. For example, a character’s health bar decreasing while accompanied by a corresponding sound effect (a pained grunt or a dramatic whoosh) instantly communicates the impact of enemy attacks. Similarly, a visual flash combined with a distinct sound can indicate the activation of a power-up or special ability. These combined cues reinforce the player’s actions and provide critical information about the game state, leading to a more intuitive and satisfying experience. In games lacking these combined cues, players might struggle to understand the consequences of their actions, leading to frustration.
Scene Description: A Crucial Gameplay Moment
Consider a stealth-action game scene where the player character is attempting to infiltrate a heavily guarded facility. As the player carefully navigates a darkened corridor, the ambient music is low and tense, building suspense. A faint creak of a nearby door accompanied by a subtle visual flicker on the screen alerts the player to the presence of a patrolling guard. The player successfully avoids detection, and the music briefly softens, offering a moment of relief before the tension builds again as the player proceeds. The combination of subtle audio cues (the creak) and visual hints (the flicker) effectively communicate environmental dangers without resorting to overly obvious indicators, increasing the sense of tension and rewarding careful play.
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, the synergy between gameplay and mechanics is the cornerstone of a successful video game. By meticulously designing core loops, carefully balancing individual mechanics, actively incorporating player feedback, and thoughtfully integrating visual and auditory elements, developers can create immersive and unforgettable gaming experiences that resonate with players long after the credits roll. A thorough understanding of these principles is essential for creating games that are both fun to play and commercially viable.
Top FAQs
What is the difference between gameplay and game mechanics?
Gameplay refers to the overall experience and how players interact with the game. Game mechanics are the specific rules, systems, and processes that govern that interaction.
How do I identify the core gameplay loop of my game?
Map out the player’s actions, rewards received, and consequences faced in a typical play session. This cycle represents the core loop.
How can I improve player feedback loops?
Implement clear visual and auditory cues, provide regular feedback on player progress, and actively solicit and respond to player feedback through surveys, forums, or in-game feedback systems.


